NodeJS – Simple CRUD APIs with MySQL
In this article, I will do a simple CRUD APIs in NodeJS, Express and MySQL. We learn how to create restful (create, read, update, delete) api in NodeJS.
API End Points, test on Postman:
- GET /learns: Give all learns stored in database
- GET /learns/{id}: Give a specific user with id.
- POST /learns : Create a record
- PUT /learns/{id}: Update a record
- DELETE /learns/{id}: Delete a record
Modules to install and use in this example:
- express.js: Web framework express.
- mysql: Node.js driver for MySQL.
- body-parser: Converting the POST data into the request body.
- nodemon: Automatically restart the server whenever the code changes.
1. Install the modules to use in NodeJS
Run [npm init] to initialize the source file, package.json. Select the js code file is index.js
npm init
Install these packages, type in the following command on Git Bash or your favorite cmd:
npm i –s express express-handlebars mysql body-parser
Installing nodemon with the global command:
npm i -g nodemon
We will have the following soure:

Source folder
Package.json file content:
{
“name”: “nodemysql”,
“version”: “1.0.0”,
“description”: “”,
“main”: “index.js”,
“scripts”: {
“test”: “echo \”Error: no test specified\” && exit 1″
},
“author”: “”,
“license”: “ISC”,
“dependencies”: {
“body-parser”: “^1.19.0”,
“express”: “^4.17.1”,
“express-handlebars”: “^5.3.0”,
“mysql”: “^2.18.1”
}
}
2. MySQL Database
Create Database learns, with node_mysql_simple table as simple as follows:
// Schema: learns, DB: node_mysql_simple
CREATE DATABASE `learns` /*DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
CREATE TABLE `node_mysql_simple` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`course_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;

MySQL Database
3. Index.js file server code
Use the required libraries that have been installed in NodeJS and establish a connection with MySQL.
const mysql = require(‘mysql’);
const express = require(‘express’);
const bodyparser = require(‘body-parser’);
var app = express();// Express server
app.use(bodyparser.json());// MySQL connection details
var mysqlConnection = mysql.createConnection({
host: ‘localhost’,
user: ‘root’,
password: ”,
database: ‘learns’,
multipleStatements: true
});mysqlConnection.connect((err) => {
if (!err) {
console.log(‘Connect success.’);
} else {
console.log(‘Connect faile: ‘ + JSON.stringify(err, undefined, 2));
}
});const port = process.env.PORT || 8080;
app.listen(port, () => console.log(`Listen on port ${port}…`));
Now you run the web server using command: node index.js
node index.js
And your server is running at port 8080.

Command run the web server
3.1. Insert data to Database, method POST route
var urlencodedParser = bodyparser.urlencoded({ extended: false });
// Post route value get from params
app.post(‘/learns’, urlencodedParser, (req, res) => {
let name = req.body.name;
let email = req.body.email;
let course_id = req.body.course_id;let sql = “INSERT INTO node_mysql_simple (name, email, course_id) VALUES (?, ?, ?)”;
mysqlConnection.query(sql, [name, email, course_id], (err, rows, fields) => {
if (!err) {
res.send(‘Inserted ID : ‘ + rows.insertId);
} else {
console.log(err);
}
})
});
– Test on Postman: Input simple data with name, email. course_id.

Method Post
Or you can use MySQL insert multiple rows from array.
// Post route direct value
app.post(‘/learnDirect’, (req, res) => {
// Multi values
let values = [
[‘Amit’, ‘amit@gmail’, 1],
[‘Rishi’, ‘rishi@gmail’, 1],
[‘Akash’, ‘akash@gmail’, 1],
];let sql = ‘INSERT INTO node_mysql_simple (name, email, course_id) VALUES ?’;
mysqlConnection.query(sql, [values], (err, rows, fields) => {
if (!err) {
res.send(‘Inserted ID ‘ + rows.insertId);
} else {
console.log(‘Error: ‘ + err);
}
});
});
3.2. Show data list and detail data with method GET route
– Get route list:
// Get route list
app.get(‘/learns’, (req, res) => {
mysqlConnection.query(‘SELECT * FROM node_mysql_simple’, (err, rows, field) => {
if (!err) {
res.send(rows);
} else {
console.log(‘Query error: ‘ + err);
}
})
});
After inserting the second record, we have the results, test on Postman:
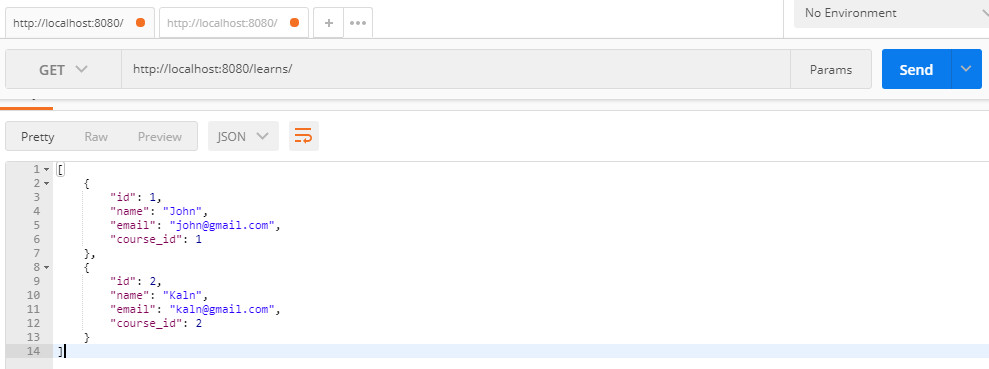
Method Get, get data list
– Get route detail:
// Get route detail
app.get(‘/learns/:id’, (req, res) => {
mysqlConnection.query(‘SELECT * FROM node_mysql_simple WHERE id = ?’, [req.params.id], (err, row, field) => {
if (!err) {
res.send(row);
} else {
console.log(‘Query error: ‘ + err);
}
})
});
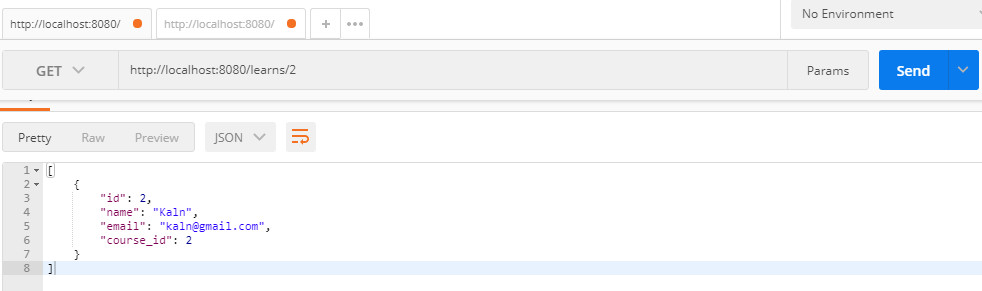
Method Get, get detail on Postman
3.3. Update data with method PUT route
// Put route value get from params
app.put(‘/learns/:id’, urlencodedParser, (req, res) => {
let id = req.params.id;let name = req.body.name;
let email = req.body.email;
let course_id = req.body.course_id;let sql = “UPDATE node_mysql_simple SET name = ?, email = ?, course_id = ? WHERE id = ?”;
mysqlConnection.query(sql, [name, email, course_id, id], (err, rows, fields) => {
if (!err) {
res.send(‘Updated with ID : ‘+ id);
} else {
console.log(err);
}
})
});

Method Update
3.4. Delete data with method Delete
// Route Delete
app.delete(‘/learns/:id’, (req, res) => {
mysqlConnection.query(‘DELETE FROM node_mysql_simple WHERE id = ?’, [req.params.id], (err, rows, fields) => {
if (!err) {
res.send(‘Delete success ID: ‘ + req.params.id);
} else {
console.log(‘Delete error: ‘ + err);
}
})
});

Method Delete
– Maybe you are interested: PHP – MVC CRUD and Connect to MySQL using PDO
Thank for reading.




Your comment